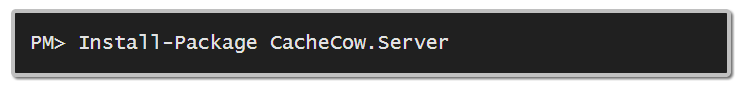
You can see other cool NuGet Packages I've mentioned on the blog here. Today's NuGet package is CacheCow, which has possibly the coolest Open Source Library name since Lawnchair.js.
"CacheCow is a library for implementing HTTP caching on both client and server in ASP.NET Web API. It uses message handlers on both client and server to intercept request and response and apply caching logic and rules."
CacheCow was started by Ali Kheyrollahi with help from Tugberk Ugurlu and the community, and is a fantastically useful piece of work. I wouldn't be surprised to see this library start showing in more places one day.
As an aside, Ali, this would be a great candidate for setting up a free AppVeyor Continuous Integration build along with a badge showing that the project is building and healthy!
CacheCow on the server can manage the cache in a number of ways. You can store it in SQL Server with the EntityTagStore, or implement your own storage handler. You can keep the cache in memcached, Redis, etc.
Consider using a library like CacheCow if you're putting together a Web API and haven't given sufficient thought to caching yet, or if you're already sprinkling cache code throughout your business logic. You might already suspect that is going to litter your code but perhaps haven't gotten around to tidying up. Now is a good time to unify your caching.
As a very simple example, here's the HTTP Headers from an HTTP GET to a Web API:
Cache-Control: no-cache
Content-Length: 19
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
Date: Fri, 27 Jun 2014 23:22:10 GMT
Expires: -1
Pragma: no-cache
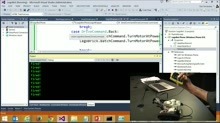
Here's the same thing after adding the most basic caching to my ASP.NET applications config:
GlobalConfiguration.Configuration.MessageHandlers.Add(new CachingHandler(GlobalConfiguration.Configuration));
The HTTP Headers with the same GET with CacheCow enabled:
Cache-Control: no-transform, must-revalidate, max-age=0, private
Content-Length: 19
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
Date: Fri, 27 Jun 2014 23:24:16 GMT
ETag: W/"e1c5ab4f818f4cde9426c6b0824afe5b"
Last-Modified: Fri, 27 Jun 2014 23:24:16 GMT
Notice the Cache-Control header, the Last-Modified, and the ETag. The ETag is weak as indicted by "W/" which means that this response is semantically equivalent to the last response. If I was caching persistently, I could get a strong ETag indicating that the cached response was byte-for-byte identical. Also, if the client was smart about caching and added If-Modified-Since or If-None-Match for ETags, the response might be a 304 Not Modified, rather than a 200 OK. If you're going to add caching to your Web API server, you'll want to make sure your clients respect those headers fully!
From ALI's blog, you can still use HttpClient in your clients, but you use WebRequestHandler as the message handler:
HttpClient client = new HttpClient(new WebRequestHandler()
{
CachePolicy = new RequestCachePolicy(RequestCacheLevel.Default)
});
var httpResponseMessage = await client.GetAsync(http://superpoopy);
Really don't want a resource cached? Remember, this is HTTP so, Cache-Control: no-cache from the client!
Of course, one of the most important aspects of caching anything is "when do I invalidate the cache?" CacheCow gives you a lot control over this, but you really need to be aware of what your actual goal is or you'll find things cache you don't want, or things not cached that you do.
- Are you looking for time-based caching? Cache for 5 min after a DB access?
- Are you looking for smart caching that invalidates when it sees what could be a modification? Invalidate a collection after a POST/PUT/DELETE?
Given that you're likely using REST, you'll want to make sure that the semantics of these caching headers and their intent is reflected in your behavior. Last-Modified should reflect realty when possible.
From the CacheCow Wiki, there's great features for both the Server-side and Client-side. Here's CacheCow.Server features
- Managing ETag, Last Modified, Expires and other cache related headers
- Implementing returning Not-Modified 304 and precondition failed 412 responses for conditional calls
- Invalidating cache in case of PUT, POST, PATCH and DELETE
- Flexible resource organization. Rules can be defined so invalidation of a resource can invalidate linked resources
and the CacheCow.Client features
- Caching GET responses according to their caching headers
- Verifying cached items for their staleness
- Validating cached items if must-revalidate parameter of Cache-Control header is set to true. It will use ETag or Expires whichever exists
- Making conditional PUT for resources that are cached based on their ETag or expires header, whichever exists
Another good ASP.NET caching library to explore is ASP.NET Web API "CacheOutput" by Filip Wojcieszyn. While it doesn't have an fun to say name ;) it's got some great features and is super easy to get started with. You can find CacheOutput with NuGet at
Install-Package Strathweb.CacheOutput.WebApi2And you'll configure your caching options using the intuitive CacheOutput attributes like those you may have seen in ASP.NET MVC:
[CacheOutput(ClientTimeSpan = 100, ServerTimeSpan = 100)]
public IEnumerable<string> Get()
{
return new string[] { "value1", "value2" };
}
ASP.NET Web API CacheOutput has great getting started docs and clear easy to ready code.
So, you've got options. Go explore!
You can also pickup the Pro ASP.NET Web API book at Amazon. Go explore CacheCow or CacheOutput and support open source! If you find issues or feel there's work to be done in the documentation, why not do it and submit a pull request? I'm sure any project would appreciate some help with updated samples, quickstarts, or better docs.
Sponsor: Many thanks to our friends at Octopus Deploy for sponsoring the feed this week. Did you know that NuGet.org deploys with Octopus? Using NuGet and powerful conventions, Octopus Deploy makes it easy to automate releases of ASP.NET applications and Windows Services. Say goodbye to remote desktop and start automating today!
© 2014 Scott Hanselman. All rights reserved.









































_c61156b1-d01c-41ac-aaf3-7ea3a8820a05.png)
_55d97716-f173-4833-bc81-07fb030b2ea0.png)

_5dccfd6f-4ea1-4706-bcbf-3fb77a65effb.png)
_c7a7a38b-4d32-4ae2-8c0d-a8e01d7fa9c9.png)


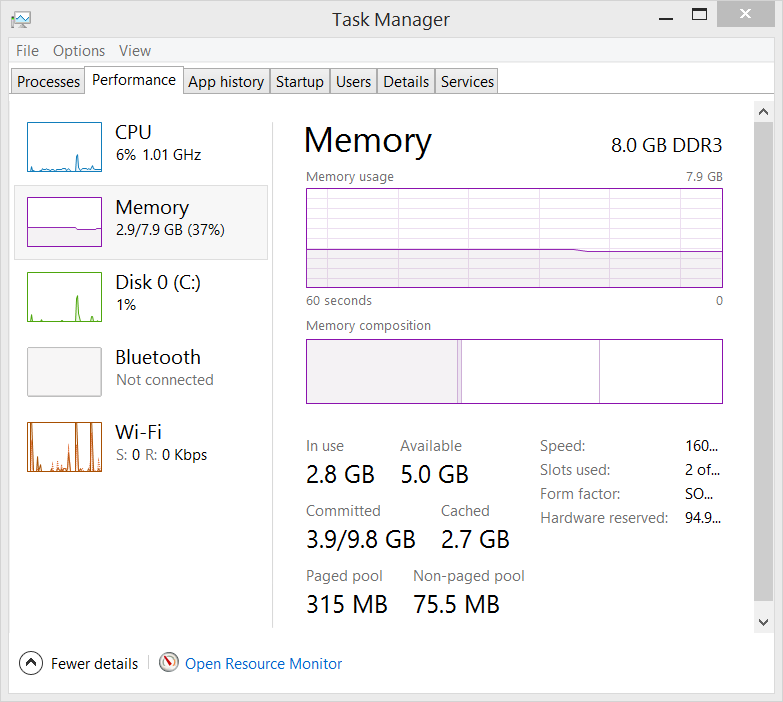
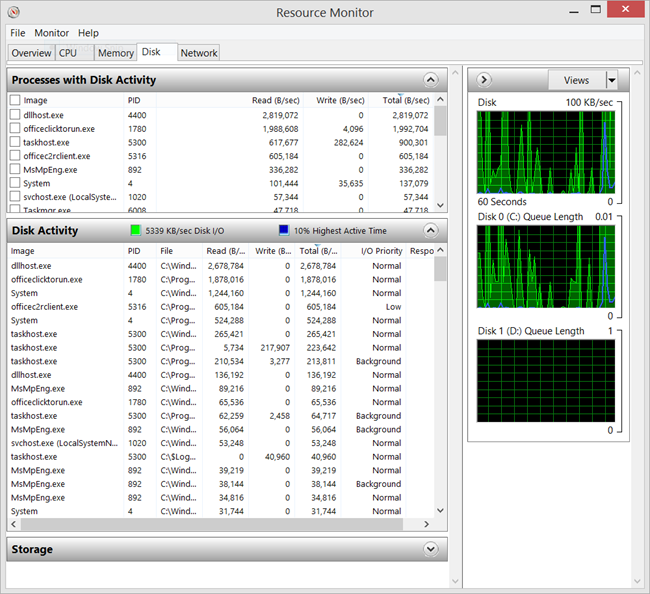
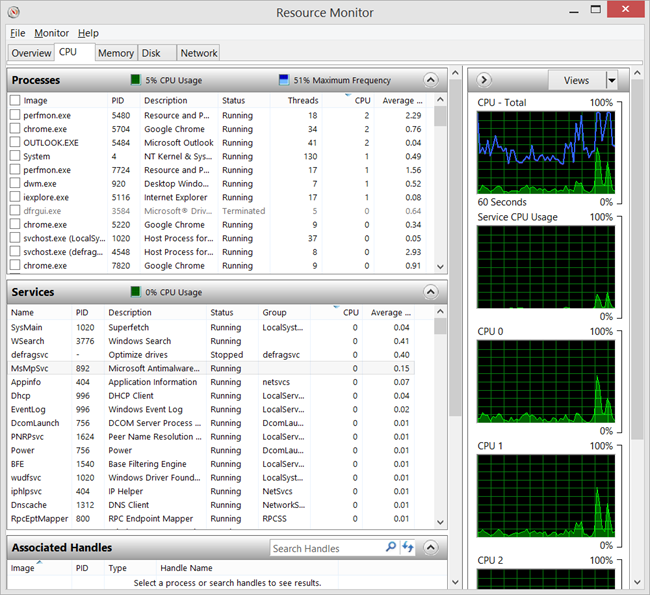
 We've got an older HP TouchSmart all in one computer that we use as the "Kitchen PC." It's basically a browsing, emails, YouTube, and recipes machine. It's lovely machine, really. I've actually seen them at Goodwill, in fact, for cheap. If you can pick one up inexpensively, I recommend it.
We've got an older HP TouchSmart all in one computer that we use as the "Kitchen PC." It's basically a browsing, emails, YouTube, and recipes machine. It's lovely machine, really. I've actually seen them at Goodwill, in fact, for cheap. If you can pick one up inexpensively, I recommend it.
 The difference between my
The difference between my