 ASP.NET and Web Tools 2012.2 is coming soon, but one of the features of ASP.NET that you can use TODAY is support for Google, Twitter, Microsoft and Facebook logins out of the box with ASP.NET templates. I show how OAuth in ASP.NET works in this 5 minute video. We are also continuing to look at ways to make membership easier in coming versions of ASP.NET like including things like this out of the box.
ASP.NET and Web Tools 2012.2 is coming soon, but one of the features of ASP.NET that you can use TODAY is support for Google, Twitter, Microsoft and Facebook logins out of the box with ASP.NET templates. I show how OAuth in ASP.NET works in this 5 minute video. We are also continuing to look at ways to make membership easier in coming versions of ASP.NET like including things like this out of the box.
Mozilla has a new identity system called Mozilla Persona that uses browserid technology to let users log in to your site without creating a custom login or username.
I wanted to see how Persona would work in ASP.NET and hacked up a prototype (with some sanity checking from my buddy Hao Kung). There's some comments and some TODOs, but it's a decent proof of concept.
First, I read the Mozilla Persona Developer docs and got their fancy button CSS, then added it all to the ExternalLoginsListPartial view.
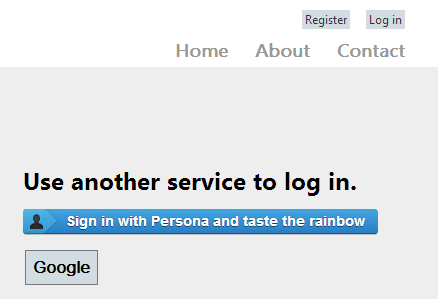
The ProviderName check is there just because all the buttons look the same except the Persona one. A better way, perhaps, would be partial views for each button, or a custom helper.
@foreach (AuthenticationClientData p in Model)
{
if(p.AuthenticationClient.ProviderName == "Persona") //ya, ya, I know.
{
if (!Request.IsAuthenticated) {
<p><a href="#" class="persona-button" id="personasignin"><span>Sign in with your Email</span></a></p>
}
<!-- The CSS for this is in persona-buttons.css and is bundled in in BundleConfig.cs -->
}else{
<button type="submit" name="provider" value="@p.AuthenticationClient.ProviderName" title="Log in using your @p.DisplayName account">@p.DisplayName</button>
}
}
After the login dialog, an AJAX call to do the login locally posts data to my new PersonaController. except it doesn't POST its assert as JSON, but rather as a simple (standard) POST value. That is, just "assertion: longvalue."
function onAssertion(assertion) {
if (assertion) {
$.ajax({ /* <-- This example uses jQuery, but you can use whatever you'd like */
type: 'POST',
url: '/api/persona/login', // This is a URL on your website.
data: { assertion: assertion, },
success: function (res, status, xhr) { window.location.reload(); },
error: function (res, status, xhr) { alert("login failure" + res); }
});
}
else {
alert('Error while performing Browser ID authentication!');
}
}ASP.NET Web API doesn't grab simple POSTs cleanly by default, preferring more formal payloads. No worries, Rick Strahl solved this problem with this clever SimplePostVariableParameterBinding attribute which allows me to just have string assertion in my method.
Armed with this useful attribute (thanks Rick!) my PersonaController login is then basically:
- Get the assertion we were given from Persona on the client side
- Load up a payload with that assertion so we can POST it back to Persona from the Server Side.
- Cool? We're in, make a local UserProfile if we need to, otherwise use the existing one.
- Set the FormsAuth cookie, we're good.
Here is the work:
[SimplePostVariableParameterBinding]
public class PersonaController : ApiController
{
// POST api/persona
[HttpPost][ActionName("login")]
public async Task<HttpResponseMessage> Login(string assertion) {
if (assertion == null) {
return new HttpResponseMessage(HttpStatusCode.BadRequest);
}
var cookies = Request.Headers.GetCookies();
string token = cookies[0]["__RequestVerificationToken"].Value;
//TODO What is the right thing to do with this?
using (var client = new HttpClient()) {
var content = new FormUrlEncodedContent(
new Dictionary<string, string> {
{ "assertion", assertion },
{ "audience", HttpContext.Current.Request.Url.Host }
//TODO: Can I get this without digging in HttpContext.Current?
}
);
var result = await client.PostAsync("https://verifier.login.persona.org/verify", content);
var stringresult = await result.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
dynamic jsonresult = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<dynamic>(stringresult);
if (jsonresult.status == "okay") {
string email = jsonresult.email;
string userName = null;
if (User.Identity.IsAuthenticated) {
userName = User.Identity.Name;
}
else {
userName = OAuthWebSecurity.GetUserName("Persona", email);
if (userName == null) {
userName = email; // TODO: prompt for custom user name?
using (UsersContext db = new UsersContext()) {
//TODO: Should likely be ToLowerInvariant
UserProfile user = db.UserProfiles.FirstOrDefault(u => u.UserName.ToLower() == userName.ToLower());
// Check if user already exists
if (user == null) {
// Insert name into the profile table
db.UserProfiles.Add(new UserProfile { UserName = userName });
db.SaveChanges();
}
}
}
}
OAuthWebSecurity.CreateOrUpdateAccount("Persona", email, userName);
FormsAuthentication.SetAuthCookie(email, false);
return new HttpResponseMessage(HttpStatusCode.OK);
}
}
return new HttpResponseMessage(HttpStatusCode.Forbidden);
}
[HttpPost][ActionName("logout")]
public void Logout() {
WebSecurity.Logout();
}
}
You click Sign in and get the Persona login dialog:
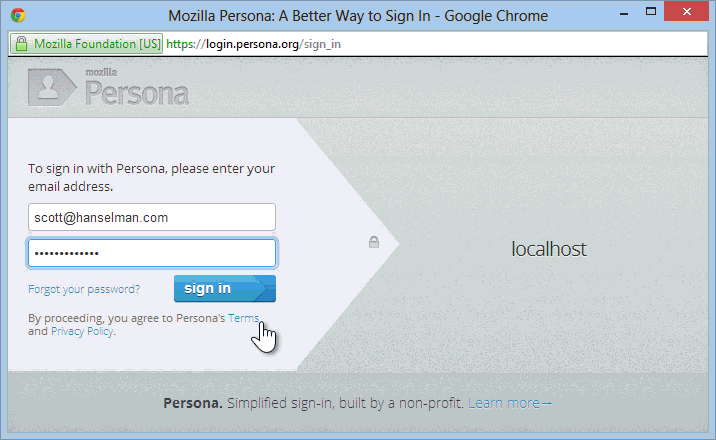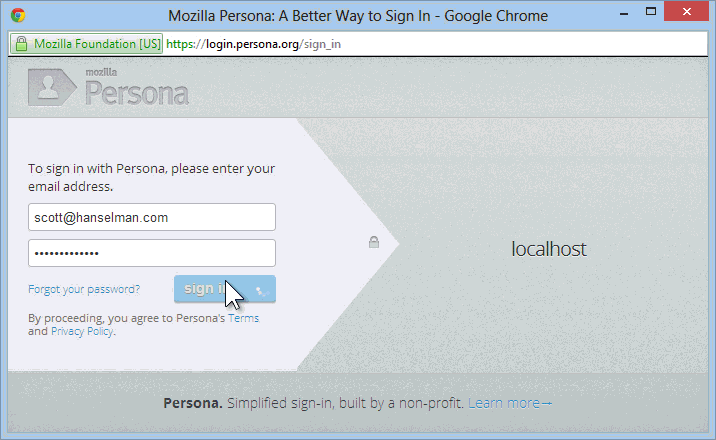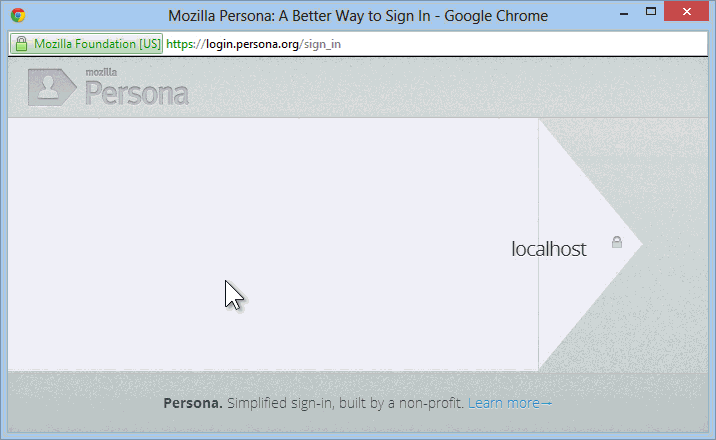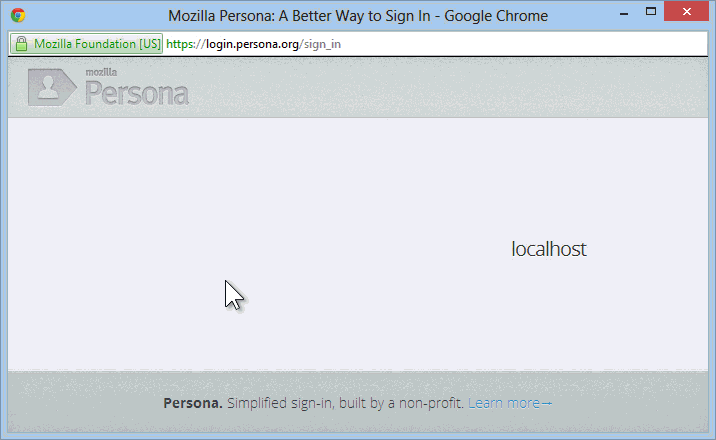
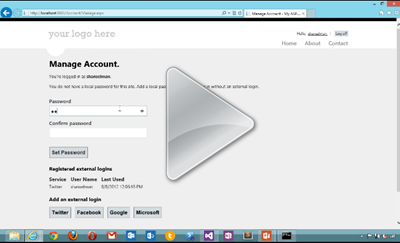
At this point, you're logged into the site with a real UserProfile, and things with ASP.NET Membership work as always. You can add more external logins (Twitter, Google, etc) or even add a local login after the fact.
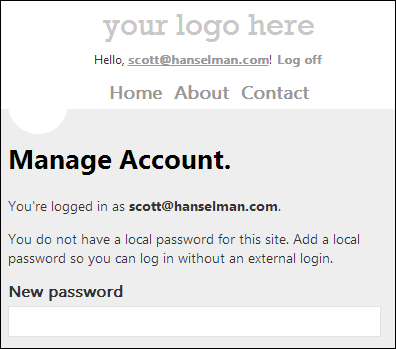
As I said, this isn't ready to go, but feel free to poke around, do pull requests, fork it, or comment on how my code sucks (in a kind and constructive way, because that's how we do things here.)
© 2013 Scott Hanselman. All rights reserved.




